How Does Printer Ink Work?
Jan 25, 2020 12:29:14 PM
The two printers that are most popular and cost-effective for common print jobs in homes and offices today are inkjet and laser printers. While inkjet printers use ink in ‘liquid’ form, laser printers use a toner in ‘powder’ form to print the desired image on a substrate. Whether you should get an inkjet or laser printer, is a topic that we’ve covered in detail in another post. Here in this post, we will discuss how printer ink (in inkjet printers) works.
Let us begin with the basics.
What is Printer Ink Made Up Of?
Printer ink has various ingredients such as pigments, resins, varnish, solvents, waxes, lubricants, etc. The black ink is generally made using carbon black pigments. Titanium dioxide, on the other hand, is often used as a white pigment.
Printer manufacturing companies or third-party manufactures of compatible ink cartridges do not share information about the exact composition of printer inks they sell. It’s a trade-secret, after all.
The two main varieties of printer ink are:
- Dye-based ink: This type of ink consists of a colorant, fully dissolved in a liquid such as water or glycol. The ink flows easily from the print head to the substrate and dries in no time once it’s there. Dye-based inks are relatively cheaper. A large number of standard inkjets that use dye-based inks produce razor-sharp text and reasonably good-looking images with vibrant colors. However, dye-based inks are more likely to smear and the prints tend to fade after five years.
- Pigment-based ink: It is made from solid particles of pigment powder, suspended in a liquid. Pigment-based ink is more durable as it resists fading for a longer duration. The colors produced by pigmented inks are not as vibrant but they are a perfect choice for printing on slicker surfaces such as stickers and transparencies.
The qualitative difference in the output produced by dye and pigment-based inks is hard to spot for inexperienced eyes.
Regardless of the type of ink an inkjet uses, there are ways to make printer ink last longer.
Where is Printer Ink Stored?
The printer ink is held in a cartridge, identified by a unique cartridge number. Different inkjet printer models work with different ink cartridges.
An ink cartridge is classified as ‘standard-yield’ or ‘high-yield’ depending upon the amount of ink it holds.
High-yield Epson or Canon printer ink cartridges, for instance, can print more as they hold more ink. Consumers who print frequently often buy high-yield ink cartridges to reduce printing costs.
A typical inkjet printer for professional use utilizes a black plus three-color ink system. The three primary colors include cyan, magenta, and yellow. The primary colors produce all other printable colors through blending. Photographers, graphic designers, and others who require high-quality prints, use inkjets that have four, five or more color-inks.
Most inkjet printers have a separate black ink cartridge. An inkjet printer may use a single cartridge that houses all colors or it may have separate ink cartridges for all colors.
Inkjet cartridges also have microchips and other small, electronic components that help control the ink spray and measure the amount of ink left.
The Print Head
An inkjet printer cartridge may or may not have an integrated print head.
- Fixed Print Head: Some printers have built-in print heads, separate from the color inkjet printer cartridges. Epson and Canon are two companies known to have offered the maximum number of printers with fixed print heads. Some of the recent models from HP, such as OfficeJet Pro 8620, also use a fixed print head.
- Disposable Print Head: In this case, the print head is supplied as part of the replaceable inkjet printer cartridge. Hewlett-Packard has generally favored disposable (separate) print heads. Canon, too, followed the same design philosophy in its early printer models.
There’s a middle path as well; companies such as Kodak offer printers with replaceable ink cartridges and separate, disposable print heads. HP’s high-volume inkjets and many of the recent models offered by Canon now use this design philosophy. The print head is intended to last the life of the printing device but users have the option to replace it if necessary.
How Does the Print Head Work?
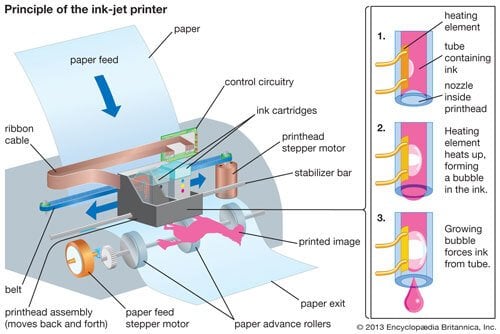
The print head consists of an array of closely-arranged microscopic nozzles that spray the ink onto a substrate such as paper, plastic film, cardboard, fabric, canvas, etc. in small, precise drops.
How the ink is sprayed onto a substrate, depends upon the underlying technology.
Most of the contemporary printers found in homes and offices use the Drop-on-Demand (DOD) technology.
DOD technology is further divided into two categories:
- Thermal Technology: A majority of consumer inkjet printers available in the market, including those from Canon, HP, and Lexmark use the thermal inkjet technology. In this case, the printer cartridge comprises of small chambers, each with a tiny, electric heater. When electricity is passed through the heating element, the ink in the chamber vaporizes and takes a bubble-form. The droplet of ink is propelled through the print head nozzle, onto the substrate due to an increase in the pressure inside the chamber. Since the ink needs to vaporize, the thermal inkjet process requires the ink to have a volatile component. A thermal inkjet print head is cheaper to produce as no special components are required.
- Piezoelectric Technology: Printers manufactured by Brother and Epson utilize piezoelectric technology. Most industrial inkjets too rely on this printing technology. Here, instead of a heating element, a piezoelectric material such as lead zirconium titanate is placed behind a nozzle on the print head. When the voltage is applied, the piezoelectric material changes its shape, pushing the ink droplet inside the ink-filled chamber, onto the substrate. A piezoelectric inkjet print head is relatively more expensive but less susceptible to clogging.
In both of these processes, it’s a software program that directs the print head to release a certain number of ink-droplets per dot.
Final Words
If you enjoyed reading’ how printer ink works,’ you may also be interested in learning how to care for your ink cartridges. After all, printer ink is expensive and you wouldn’t want an ink cartridge to go waste.
In case you are wondering ‘what to do with used ink cartridges,’ head straight to our ‘Recycle Ink Cartridges’ section and learn how you can get a $10 coupon for recycling an ink cartridge through InkjetsClub!

Comments